# 08-整合Redis
在 Redis 出现之前,我们的缓存框架各种各样,有了 Redis ,缓存方案基本上都统一了。
关于 Redis,这里有一个系列教程,尚不了解 Redis 的小伙伴可以参考这个教程:Redis 教程合集 (opens new window)
使用 Java 操作 Redis 的方案很多,Jedis 是目前较为流行的一种方案,除了 Jedis ,还有很多其他解决方案,如下:
# 一、Spring Boot 中常用Redis操作方案
1. Spring Data Redis(推荐)
在传统的 SSM 中,开发者需要自己来配置 Spring Data Redis,这个配置比较繁琐,主要配置 3 个东西:连接池、连接器信息以及 key 和 value 的序列化方案。
而到了Spring Boot时代,官方默认集成的 Redis 就是 Spring Data Redis,就是为了让广大的开发者更加简单方便的来操作Redis。
2. Spring Cache
通过 Spring Cache 的形式来操作 Redis,Spring Cache 统一了缓存江湖的门面,这种方案有专门的文章介绍,小伙伴可以移步这里:Spring Boot中,Redis缓存还能这么用! (opens new window)。
3. 直接使用Redis客户端
直接使用 Jedis 或者 其他的客户端工具来操作 Redis ,这种方案在 Spring Boot 中也是支持的,虽然操作麻烦,但是支持,这种操作也有相关介绍的文章,因此这里就不再赘述了,可以参考 Jedis 使用 (opens new window)。
这里总结了三种方案,事实上前两个使用更广泛一些,直接使用 Jedis 还是比较少,基本上 Spring Boot 中没见过有人直接这么搞。
而前两种方案中,第一种方案在Spring Boot中,集成会更加的简单、方便,所以接下来的这篇文章我们就以这种方式来进行详细讲解。
# 二、集成 Spring Data Redis
在 Spring Boot 中,默认集成的 Redis 就是 Spring Data Redis,默认底层的连接池使用了 lettuce ,开发者可以自行修改为自己的熟悉的,例如 Jedis。
Spring Data Redis 针对 Redis 提供了非常方便的操作模板 RedisTemplate 。这是 Spring Data 擅长的事情,那么接下来我们就来看看 Spring Boot 中 Spring Data Redis 的具体用法。
# 新建项目
创建maven项目,引入 Redis 相关依赖。另外,还需要手动引入 commos-pool2 的依赖,因此最终完整的 pom.xml 依赖如下:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
这里主要就是引入了 Spring Data Redis + 连接池。
# 配置 Redis
接下来配置 Redis 的信息,主要包括两方面,一方面是 Redis 的基本信息,另一方面则是连接池信息:
spring.redis.database=0
spring.redis.password=123
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.host=192.168.66.128
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=5
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=10
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=1ms
spring.redis.lettuce.shutdown-timeout=100ms
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 自动配置
当开发者在项目中引入了 Spring Data Redis ,并且配置了 Redis 的基本信息,此时,自动化配置就会生效。
我们从 Spring Boot 中 Redis 的自动化配置类中就可以看出端倪:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(RedisOperations.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class)
@Import({ LettuceConnectionConfiguration.class, JedisConnectionConfiguration.class })
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
这个自动化配置类很好理解:
- 首先标记这个是一个配置类,同时该配置在 RedisOperations 存在的情况下才会生效(即项目中引入了 Spring Data Redis)
- 然后导入在 application.properties 中配置的属性
- 然后再导入连接池信息(如果存在的话)
- 最后,提供了两个 Bean,
RedisTemplate和StringRedisTemplate。其中 StringRedisTemplate 是 RedisTemplate 的子类,两者的方法基本一致,不同之处主要体现在操作的数据类型不同。RedisTemplate 中的两个泛型都是 Object ,意味者存储的 key 和 value 都可以是一个对象。而 StringRedisTemplate 的 两个泛型都是 String,意味者 StringRedisTemplate 的 key 和 value 都只能是字符串。如果开发者没有提供相关的 Bean,这两个配置就会生效,否则不会生效。
# 测试类
注入 StringRedisTemplate 或者 RedisTemplate 来使用
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class RedisTest {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
public void testRedis() {
String key = "hello";
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
//设置数据
ops.set(key, "你好");
//获取数据
String value = (String) ops.get(key);
System.out.println(value);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Redis 中的数据操作,大体上来说,可以分为两种:
- 针对 key 的操作,相关的方法就在 RedisTemplate 中
- 针对具体数据类型的操作,相关的方法需要首先获取对应的数据类型,获取相应数据类型的操作方法是 opsForXXX
调用该方法就可以将数据存储到 Redis 中去了,执行代码后,我们看一下redis:
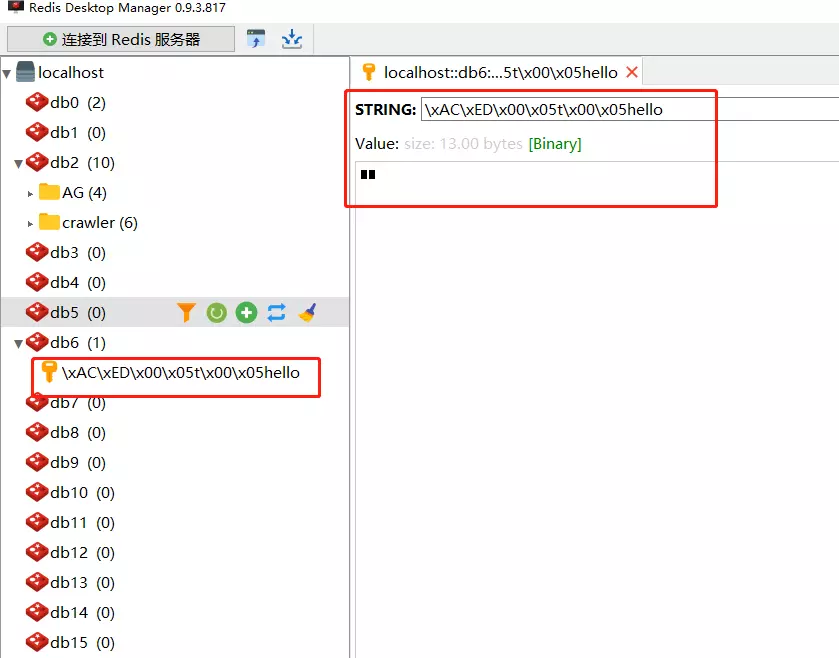
这里存在一个问题:
默认的存储方式导致 key 在Redis-Manager里面显示出来是乱码的,并且存储结果(value)是二进制了。这样不利于我们查看redis里面的数据。
为什么会出现这个问题呢?
在 RedisTemplate 中,key 默认的序列化方案是
JdkSerializationRedisSerializer。 而在 StringRedisTemplate 中,key 默认的序列化方案是StringRedisSerializer。 因此,如果使用 StringRedisTemplate,默认情况下 key 前面不会有前缀。
不过开发者也可以自行修改 RedisTemplate 中的序列化方案,如下:
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class RedisTest {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
public void hello() {
String key = "hello";
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set(key, "你好");
Object value = ops.get(key);
System.out.println(value);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
当然也可以直接使用 StringRedisTemplate:
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class RedisTest {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Test
public void hello2() {
String key = "hello";
ValueOperations ops = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set(key, "你好");
Object value = ops.get(key);
System.out.println(value);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
另外需要注意的是,Spring Boot 的自动化配置,只能配置单机的 Redis。如果是 Redis 集群,则所有的东西都需要自己手动配置。
关于如何操作 Redis 集群,以后再来和大家分享。
# 解决RedisTemplate默认序列化的问题
从上面的案例中可以看出,默认的序列化,会导致key和value都变得不那么易于理解。虽然可以在使用时设置序列化规则,但是每次都进行设置,也是比较麻烦的。接下来,我们就通过一个全局的配置,来解决这个序列化问题。
首先来完善一下maven依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
定义RedisConfig类:
/**
* redis配置
*
* 主要是配置Redis的序列化规则,替换默认的jdkSerializer
* key的序列化规则用StringRedisSerializer
* value的序列化规则用Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
// 使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerialize替换默认序列化
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
objectMapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
// 设置key和value的序列化规则
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
删除之前的key,重新执行一下test方法:
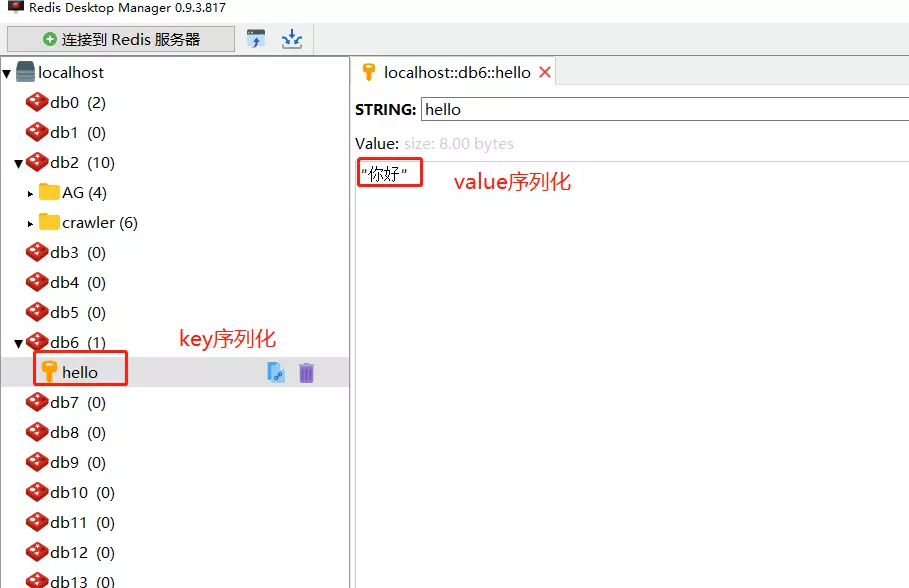
下面来演示一下SpringBoot使用RedisTemplate进行redis数据的操作。
# 三、数据操作(key/list/hash)
RedisTemplate内置redis操作如下:
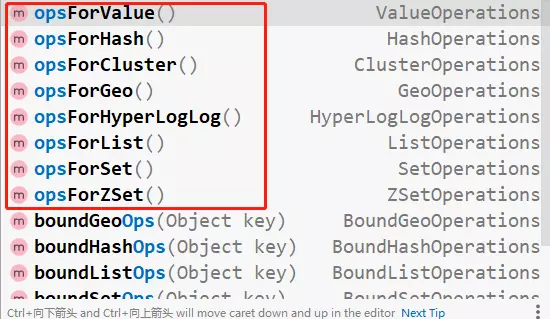
这里主要展示value/hash/list三种用法:
# 3.1 RedisTemplate.opsForValue
@Test
public void testKeyOps() {
// 测试redis操作key-value形式
Set<String> keySet = new HashSet<>();
String key1 = "name";
keySet.add(key1);
// 存储简单的key-value,并设置过期时间
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key1, "eknown", 1, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
String key2 = "token:user1";
String key3 = "token:user2";
keySet.add(key2);
keySet.add(key3);
//
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key2, "{\"name\":\"eknown\"}, \"role\":\"admin\"");
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key3, "{\"name\":\"test\"}, \"role\":\"test\"");
// 根据key的集合获取多个value
List<String> valueList = redisTemplate.opsForValue().multiGet(keySet);
for (String value : valueList) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
执行结果:
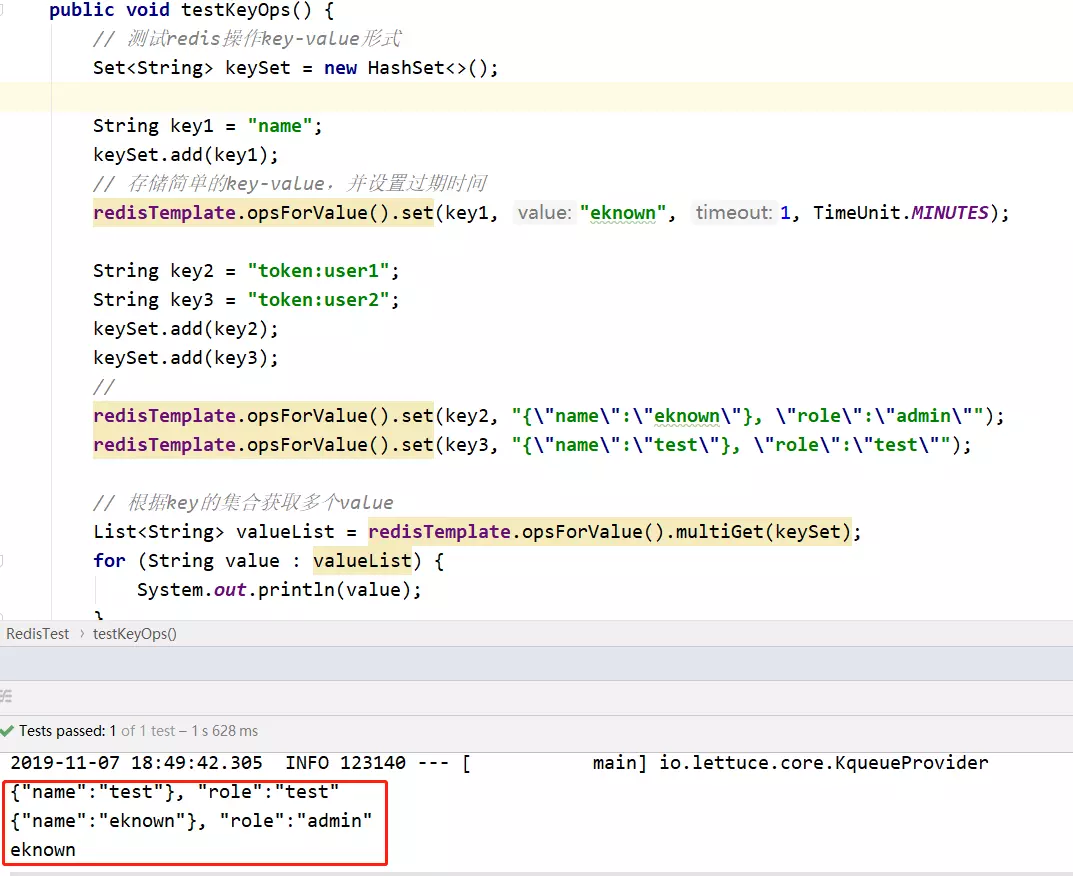
redis中的数据:
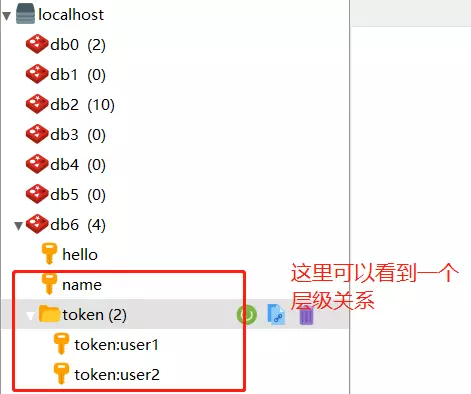
redis中的key显示出了一个层级关系,这个小技巧对于实际项目有个非常好的作用:通过prefix:suffix这样的形式,可以将redis中存储的数据分出层级。
# 3.2 RedisTemplate.opsForHash
清空该database下的数据,测试redisTemplate.opsForHash:
@Test
public void testHashOps() {
String key = "hash";
// 单次往hash中存放一个数据
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, "1", "你好");
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("2", "hello");
map.put("3a", "china1=2");
// 一次性向hash中存放一个map
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, map);
// 获取hash下的所有key和value
Map<String, Object> resultMap = redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);
for (String hashKey : resultMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println(hashKey + ": " + resultMap.get(hashKey));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
执行结果:
redis:
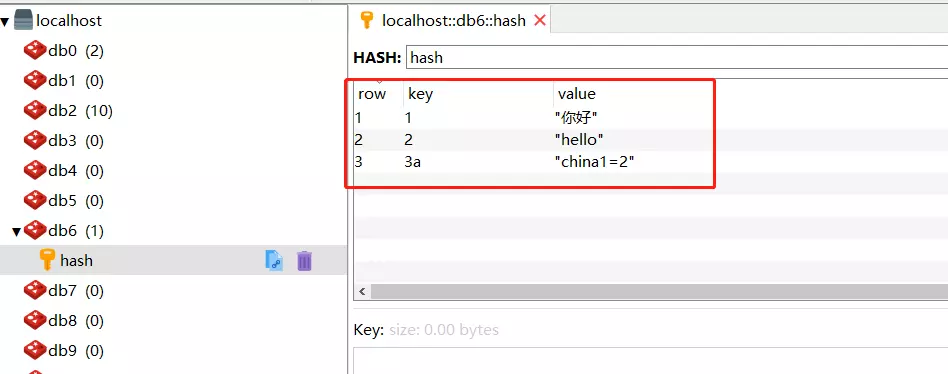
# 3.3 RedisTemplate.opsForList
@Test
public void testListOps() {
String listKey = "list";
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(listKey, "first value"); // 从list最左边插入数据
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(listKey, "second value but left");
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(listKey, 3); // 从list最右边插入数据
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("hello");
list.add("http://www.eknown.cn");
list.add(23344);
list.add(false);
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(listKey, list); // 从list右边批量插入数据
long size = redisTemplate.opsForList().size(listKey);
if (size > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < size -1 ; i++) {
// 从list最左边开始读取list中的数据,注意pop会导致出栈,也就是数据被取出来了(redis中就没有这个值了)
// 此处我们读取size-1条数据,仅留下最后一条数据
System.out.println(i + ":" + redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(listKey).toString());
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
执行上面的脚本,注意在最后的读取list数据代码前面加一个断点,此时redis中是这样的:
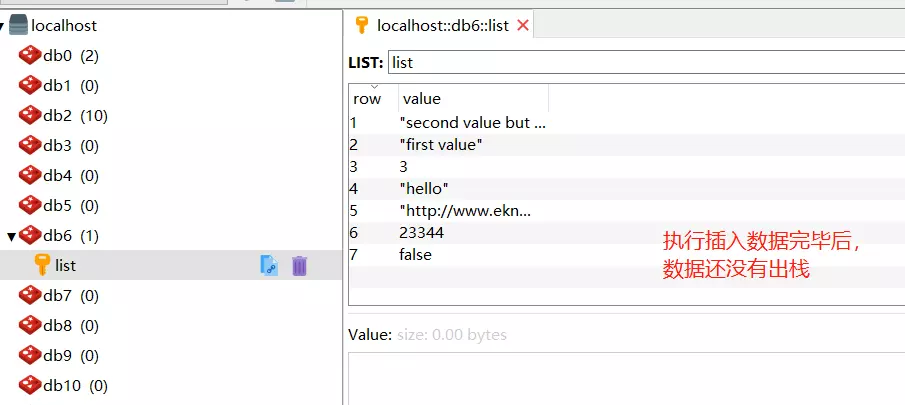
放开断点,程序继续执行,控制台如下:
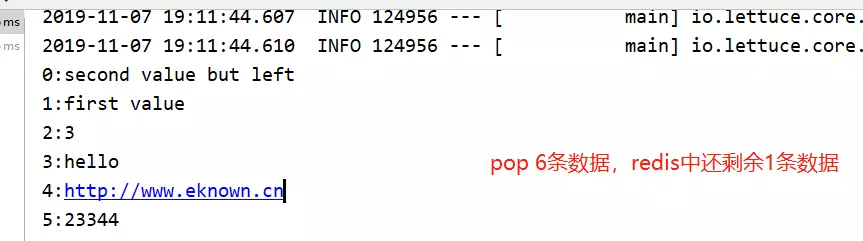
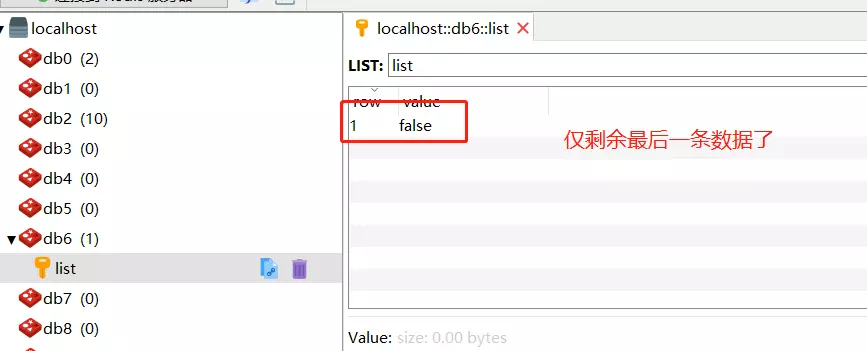
注意,此时redis中仅剩余最后一条数据,这是由于pop的问题,list中的数据被读取并删除了:
好了,这一节主要讲了SpringBoot引入redis,以及使用redis的一些基本操作和相关技巧,在此基础上,我们可以让我们的项目变得更加快速、灵活!